Air Pollution

What is Air Pollution?
Air pollution is one of the biggest threats for the environment and affects everyone: humans, animals, crops, cities, forests, aquatic ecosystems…
Air pollution can be defined as an alteration of air quality that can be characterized by measurements of chemical, biological or physical pollutants in the air. Therefore, air pollution means the undesirable presence of impurities or the abnormal rise in the proportion of some constituents of the atmosphere. It can be classified in 2 sections: visible and invisible air pollution.

Local.
this concerns the quality of ambient air within a radius of a few kilometers
Regional.
pollution like acid rain, photo chemical reactions and degradation of water quality at distances of a few kilometers to a thousand kilometers
Global.
depletion of the ozone layer and global warming caused by the emission of greenhouse gases, mainly carbon dioxide (CO2).
Air pollution causes
Air pollution is caused by the presence in the atmosphere of toxic substances, mainly produced by human activities, even though sometimes it can result from natural phenomena such as volcanic eruptions, dust storms and wildfires, also depleting the air quality.
Anthropogenic air pollution sources are:
- 1.Combustion of fossil fuels, like coal and oil for electricity and road transport, producing air pollutants like nitrogen and sulfur dioxide
- 2.Emissions from industries and factories, releasing large amount of carbon monoxide, hydrocarbon, chemicals and organic compounds into the air
- 3.Agricultural activities, due to the use of pesticides, insecticides, and fertilizers that emit harmful chemicals
- 4.Waste production, mostly because of methane generation in landfills



Air pollutioneffects
It is impossible to describe the whole extent of potential and actual damage caused by all forms of air pollution. But here are the main consequences:
ON THE ENVIRONMENT
Air pollution has a major impact on the process of plant evolution by preventing photosynthesis in many cases, with serious consequences for the purification of the air we breathe. It also contributes to the formation of acid rain, atmospheric precipitations in the form of rain, frost, snow or fog, which are released during the combustion of fossil fuels and transformed by contact with water steam in the atmosphere.

GLOBAL WARMING
On top of that, air pollution is a major contributor to global warming and climate change. In fact, the abundance of carbon dioxide in the air is one of the causes of the greenhouse effect. Normally, the presence of greenhouse gases should be beneficial for the planet because they absorb the infra-red radiation produced by the surface of the earth. But the excessive concentration of these gases in the atmosphere is the cause of the recent climate change.

ON HUMAN HEALTH
Our continual exposure to air pollutants is responsible for the deterioration of human health.
Air pollution is indeed a significant risk factor for human health conditions, causing allergies, respiratory and cardiovascular diseases as well as lung damage.

Why is there a lid over that smog?
The gray smog pictured above is stuck between two layers of air. The bottom layer is more dense than the top layer, so there is no mixing between the two layers. In winter, an inversion traps all of the pollutants that are emitted into the air over a region.
Types of Air Pollution
The two types of air pollutants are primary pollutants, which enter the atmosphere directly, and secondary pollutants, which form from a chemical reaction.
Primary Pollutants
Some primary pollutants are natural, such as volcanic ash. Dust is natural but exacerbated by human activities; for example, when the ground is torn up for agriculture or development. Most primary pollutants are the result of human activities, the direct emissions from vehicles and smokestacks. Primary pollutants include:
- Carbon oxides include carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2) (Figure below). Both are colorless, odorless gases. CO is toxic to both plants and animals. CO and CO2 are both greenhouse gases.
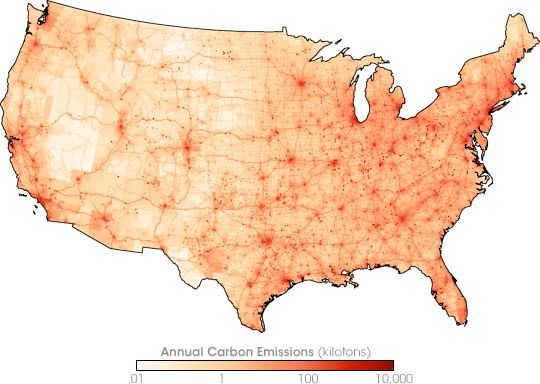
High CO2 levels are found in major metropolitan areas and along the major interstate highways.
- Nitrogen oxides are produced when nitrogen and oxygen from the atmosphere come together at high temperatures. This occurs in hot exhaust gas from vehicles, power plants, or factories. Nitrogen oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) are greenhouse gases. Nitrogen oxides contribute to acid rain.
- Sulfur oxides include sulfur dioxide (SO2) and sulfur trioxide (SO3). These form when sulfur from burning coal reaches the air. Sulfur oxides are components of acid rain.
- Particulates are solid particles, such as ash, dust, and fecal matter (Figure below). They are commonly formed from combustion of fossil fuels, and can produce smog. Particulates can contribute to asthma, heart disease, and some types of cancers.

Particulates from a brush fire give the sky a strange glow in Arizona.[
- Lead was once widely used in automobile fuels, paint, and pipes. This heavy metal can cause brain damage or blood poisoning.
- Volatile organic compound (VOCs) are mostly hydrocarbons. Important VOCs include methane (a naturally occurring greenhouse gas that is increasing because of human activities), chlorofluorocarbons (human-made compounds that are being phased out because of their effect on the ozone layer), and dioxin (a byproduct of chemical production that serves no useful purpose, but is harmful to humans and other organisms).
Secondary Pollutants
Any city can have photo chemical smog, but it is most common in sunny, dry locations. A rise in the number of vehicles in cities worldwide has increased photo chemical smog. Nitrogen oxides, ozone, and several other compounds are some of the components of this type of air pollution.
Photo chemical smog forms when car exhaust is exposed to sunlight. Nitrogen oxide is created by gas combustion in cars and then into the air (Figure below). In the presence of sunshine, the NO2 splits and releases an oxygen ion (O). The O then combines with an oxygen molecule (O2) to form ozone (O3). This reaction can also go in reverse: Nitric oxide (NO) removes an oxygen atom from ozone to make it O2. The direction the reaction goes depends on how much NO2 and NO there is. If NO2 is three times more abundant than NO, ozone will be produced. If nitric oxide levels are high, ozone will not be created.

The brown color of the air behind the Golden Gate Bridge is typical of California cities, because of nitrogen oxides.[
Ozone is one of the major secondary pollutants. It is created by a chemical reaction that takes place in exhaust and in the presence of sunlight. The gas is acrid-smelling and whitish. Warm, dry cities surrounded by mountains, such as Los Angeles, Phoenix, and Denver, are especially prone to photo chemical smog. Photo chemical smog peaks at midday on the hottest days of summer. Ozone is also a greenhouse gas.
Summary
- There are many types of primary pollutants, including carbon oxides, nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, particulates, lead, and volatile organic compounds.
- Secondary pollutants form from chemical reactions that occur when pollution is exposed to sunlight.
- Ozone is a secondary pollutant that is also a greenhouse gas.
Review
- How are primary and secondary pollutants different?
- Explain how nitrogen oxide pollutants form.
- What is ozone and how does it form as part of photochemical smog?